Choosing between LiFePO4 (lithium iron phosphate) and VRLA (valve-regulated lead-acid) batteries involves understanding the trade-offs across multiple dimensions. This comparison aims to provide clarity for informed decision-making.
Physical Characteristics
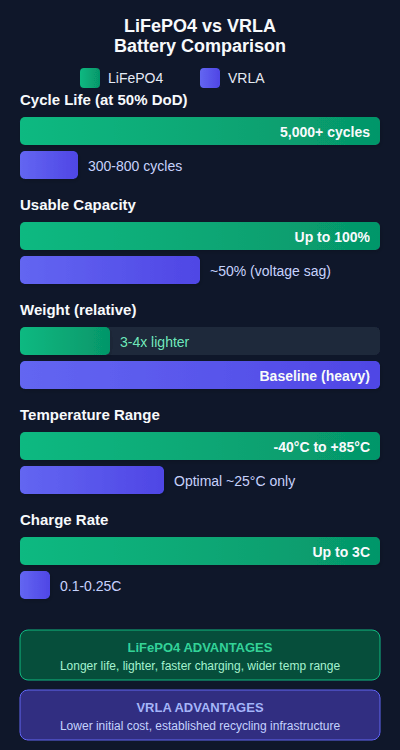
LiFePO4 batteries offer significant advantages in size and weight:
- 3-4 times lighter than equivalent VRLA batteries
- Substantially more compact form factor
- Greater flexibility in mounting orientation
- Reduced structural requirements for installations
Performance Comparison
Cycle Life
The difference in cycle life is substantial:
[Table content - see original article]
Usable Capacity
LiFePO4 provides up to double the usable capacity in high-discharge applications due to:
- Flatter discharge curve
- Better performance at high discharge rates
- Less capacity loss at low temperatures
Charging & Discharge Rates
[Table content - see original article]
Operating Conditions
Temperature Performance
LiFePO4 demonstrates superior temperature resilience:
- Operating range: -40°C to 85°C without significant degradation
- VRLA at -20°C to -40°C may deliver only 20% capacity
- High temperature accelerates VRLA degradation
Thermal Stability
A key safety advantage of LiFePO4:
- No thermal runaway characteristic
- More stable chemistry under abuse conditions
- Reduced fire risk compared to other lithium chemistries
Maintenance Requirements
[Table content - see original article]
Installation Flexibility
LiFePO4 can be mounted in any orientation including inverted positions, offering:
- Space-saving installation options
- Simplified rack design
- Reduced footprint requirements
Environmental Considerations
Manufacturing Impact
[Table content - see original article]
Lifetime Carbon Footprint
Despite higher manufacturing emissions, LiFePO4's superior lifespan results in 70-90% lower lifetime carbon footprint per cycle.
Recycling
- Lead recycling rates exceed 99% in developed nations
- LiFePO4 recycling infrastructure remains developing, currently below 5% recovery
- Both technologies require proper end-of-life handling
Cost Considerations
While LiFePO4 has higher upfront costs:
- Lower total cost of ownership over system life
- Reduced maintenance expenses
- Longer replacement intervals
- Better residual value
Selection Guidance
Consider VRLA when:
- Initial budget is constrained
- Established recycling infrastructure is important
- Application has low cycle requirements
- Temperature environment is controlled
Consider LiFePO4 when:
- Cycle life is a primary concern
- Space or weight is limited
- Temperature extremes are expected
- Low maintenance is valued
- Total cost of ownership matters more than initial cost
Conclusion
Both technologies have valid applications. The choice depends on specific project requirements, budget constraints, and operational priorities. We're happy to discuss which technology best suits your particular application.
For project-specific guidance, please contact us.
